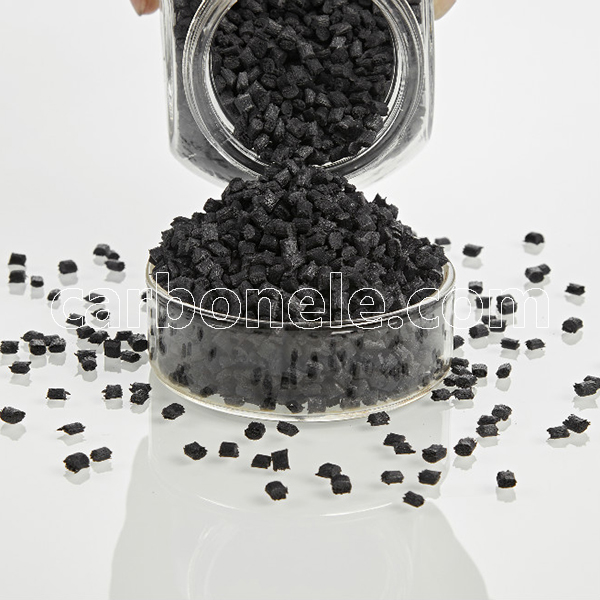
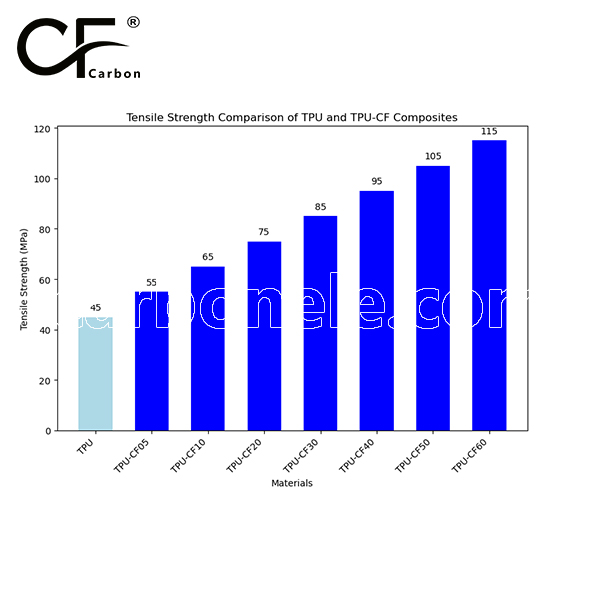
TPU-CF20 is a thermoplastic polyurethane reinforced with 20% carbon fiber, offering enhanced tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance while maintaining TPU’s flexibility. It provides excellent wear resistance and high-temperature performance, making it ideal for automotive parts, industrial equipment, and high-performance consumer goods.

TPU-CF20: High Strength Carbon Fiber Reinforced Material
- Model number: TPU-CF-BCA2
- Matrix Resin: Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
- Reinforcing Filler: Carbon fiber
- Appearance: Granules
- Grade: Injection/extrusion grade
- Packaging: 25kgs/bag
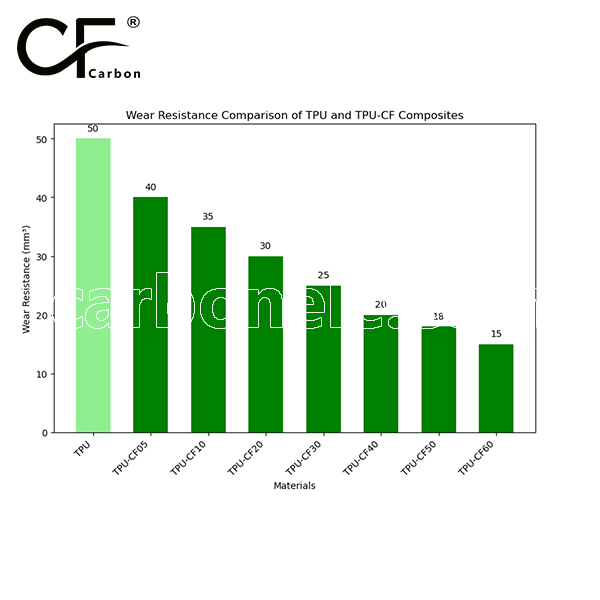
Friction coefficient of TPU-CF
The friction coefficient of TPU is typically between 0.3 and 0.5, while TPU-CF, with added carbon fiber, lowers the friction coefficient to between 0.2 and 0.4. The smaller the value, the better the wear resistance. Therefore, TPU-CF generally offers better wear resistance than pure TPU, especially under high-load conditions.

Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.