What Is Different Between PP And PP-CF? - Carbon Fiber Compounds Manufacturer | Supplier
Oct-25-2024
Differences Between PP and PP-CF.
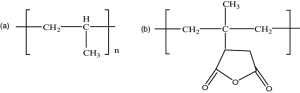
Chemical structure of (a) polypropylene and (b) CF-PP
-
Composition:
- PP (Polypropylene): A thermoplastic polymer made from propylene monomers, recognized for its versatility, lightweight nature, and ease of processing.
- PP CF (Polypropylene Carbon Fiber Composite): A composite material that enhances polypropylene with carbon fibers, significantly improving its mechanical properties.
-
Mechanical Properties:
- PP: Offers moderate tensile and flexural strength suitable for various general-purpose applications.
- PP CF: Incorporation of carbon fibers greatly enhances tensile and flexural strength, making it stronger and stiffer than standard polypropylene.
-
Weight:
- PP: While lightweight, it may not perform as well under high-load conditions.
- PP CF: Retains a low weight while providing improved strength, making it ideal for weight-sensitive applications, particularly in automotive and aerospace sectors.
-
Stiffness:
- PP: Generally less rigid, making it more susceptible to deformation.
- PP CF: The carbon fibers increase rigidity, allowing the material to maintain its shape and resist deformation under stress.
-
Impact Resistance:
- PP: Provides basic impact resistance but may not withstand severe conditions.
- PP CF: Demonstrates superior impact resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications requiring durability.
-
Chemical Resistance:
- PP: Known for excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it versatile for various applications.
- PP CF: Retains the chemical resistance of polypropylene while offering enhanced strength, ideal for industrial settings where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
-
Moisture Absorption:
- PP: Exhibits moderate moisture absorption, potentially affecting its dimensional stability in humid conditions.
- PP CF: Typically has lower moisture absorption rates, maintaining dimensional stability and mechanical properties.
Applications of PP-CF
1. Automotive Components:
- PP CF5: Used for lightweight interior parts, such as dashboards and trims, balancing strength with cost-effectiveness.
- PP CF10: Ideal for structural components requiring higher strength and impact resistance, enhancing vehicle safety.
- PP CF20: Suitable for exterior parts, offering resistance to environmental factors while maintaining performance.
2. Industrial Products:
- PP CF20: Applied in machinery parts and housings that need enhanced durability and stiffness for long-term use.
- PP CF30: Used in tools requiring high performance under stress, along with better chemical resistance.
- PP CF40: Ideal for industrial applications where superior mechanical properties are critical, such as manufacturing equipment.
3. Consumer Goods:
- PP CF5: Commonly used in luggage and sporting equipment, providing a lightweight yet durable solution.
- PP CF20: Perfect for high-end household items, ensuring both strength and aesthetic appeal.
- PP CF30: Applied in premium consumer products demanding high performance, such as advanced electronics casings.
4. Aerospace:
- PP CF30: Suitable for lightweight components needing high strength and rigidity, contributing to overall weight reduction in aircraft.
- PP CF40: Designed for critical structural parts in aerospace, offering maximum durability and reliability under extreme conditions.
- PP-CF60: Utilized in advanced aerospace applications where the highest levels of strength and performance are required.
Summary
In summary, the differences between PP and PP-CF are significant, particularly in terms of mechanical properties, weight, and applications. PP-CF offers enhanced strength, rigidity, and impact resistance, making it ideal for demanding environments. Different grades of PP-CF—such as PP-CF5, PP-CF10, and PP-CF20—cater to various industrial needs, including automotive, industrial products, consumer goods, and aerospace applications. With the integration of carbon fibers, PP-CF is positioned as a versatile solution for performance-driven applications across multiple sectors.
Feature Product
-
PA12 LCF30 for Drone Fuselages & Wings
What do you know about PA12 LCF30? PA12 ...
-
Competitive Price PA6 LCF30 Composites
What’s it? PA6 LCF30, which stands...
-
ABS CF10 Compound ABS 10%CF Thermoplastic Compo...
What’s ABS CF10? ABS CF10 refers t...