Introduction To The Molding Process And Application Of Thermoplastic Composites - Carbon Fiber Compounds Manufacturer | Supplier
The performance and quality of goods in contemporary industrial production depend much on the developments of materials science. Thermoplastic composites have progressively taken the stage in several sectors as high-performance, lightweight, durable materials become more sought for worldwide. Thermoplastic composites, a new kind of composite material, are extensively employed in aerospace, automotive manufacture, electronics and other sectors not only because of their great strength and stiffness but also because of their outstanding flexibility and recyclability.
Furthermore, in recent years the molding technique of thermoplastic composites has advanced significantly. From conventional injection molding to more sophisticated hot pressing molding, every technique has significance in certain application situations. But as application areas grow, the manufacturing cost, processing challenges, and environmental effect of thermoplastic composites have all become pressing issues needing solutions. Thus, in-depth investigation of the molding process of thermoplastic composites and their application possibilities is of major relevance to enhance the progress of materials science and fulfill industrial demands.
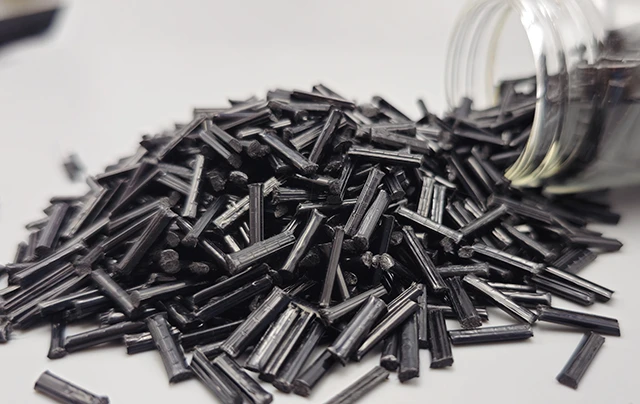

LCF reinforced thermoplastics
Thermonastic composites’ molding technique
Thermoplastic composites’ molding method mostly consists of hot pressing molding, compression molding, and injection molding. These procedures fit for many application situations and offer benefits and drawbacks of their own. The material is melted by heating and injected into the mold in the injection molding process, then cooled to produce the required shape. Although the mold design is complicated and the first cost is considerable, this rapid procedure is appropriate for large-scale manufacturing. Under great pressure, the material is placed into a warmed mold and compressed into form.
This approach is appropriate for the production of thicker and bigger pieces; the mechanical qualities of the result are decent. A quite recent technique called hot press molding stacks prefabricated composite materials and shapes them under high temperature and pressure. This procedure is appropriate for the production of intricate structural elements and may help to better regulate the fiber direction and number of layers of the material. In useful applications, different molding techniques offer certain special benefits. Because of its great efficiency and high accuracy, injection molding is extensively used in the production of tiny components like car interior parts and electronic device housings.
Large-sized components, including structural sections in aircraft, are better suited for compression molding. Excellent interlayer performance and controllability of hot press molding make it a popular method utilized in the production of high-performance and high-precision structural elements. These procedures vary greatly in material use efficiency, molding speed, manufacturing cost, etc.; so, while selecting, one should consider them in line with particular application criteria.
broad use of thermoplastic composites
Thermoplastic composites’ great qualities—high strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance—have made them very common in many different sectors. Thermoplastic composites are produced in the aerospace industry to provide structural elements like wings and fuselage panels. These components must have low weight to increase aircraft’s fuel economy in addition to satisfying high strength criteria. Thermoplastic composites are produced in the automobile sector to create body components, chassis and interior trimming. This enhances vehicle impact resistance and safety in addition to helping to light the whole weight of the vehicle and increase fuel efficiency.
Furthermore in the sector of electronic appliances, thermoplastic composites are extensively utilized to produce connectors, other components, and electronic device housings because of their great electrical insulation and heat resistance. The application fields of thermoplastic composites are still growing as technology develops constantly. This material is utilized in medical device fabrication to create robust and lightweight medical device housings as well as for even orthopedic appliances and implants.
Thermoplastic composites are produced in the construction sector to create beautiful items and high-strength building constructions, therefore enhancing the general performance and service lifetime of buildings. As environmental protection criteria have evolved, recyclability of thermoplastic composites has progressively attracted attention. It may eventually replace conventional materials in additional sectors and take increasing importance.
Advantages and Challenges of Thermoplastic Composites
Thermoplastic composites are much better than conventional materials in many respects. They are first somewhat recyclable and plastic in nature. Thermoplastic composites clearly help environmental conservation and resource use as they may be softened once again throughout the manufacturing process by heating and recycled into fresh forms.
Second, appropriate for uses in harsh settings like maritime engineering, chemical equipment, etc., thermoplastic composites have great chemical and corrosion resistance. Furthermore, this material is low in weight and strong, which may satisfy application situations with tight criteria on material attributes, including aerospace and high-performance vehicle manufacture. Still, thermoplastic composites have some difficulties.
First, particularly in high-precision and high-performance applications, the high cost of its manufacturing process results from the complexity of the molding technique raising production expenses. Second, thermoplastic composites’ processing technologies have significant equipment and technological needs, which might create certain technical obstacles for small and medium-sized businesses. Furthermore, the high melting temperature of the substance requires exact control of temperature and pressure during processing to guarantee the quality and performance of the resultant good.

carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites
Conclusion
Thermoplastic composites, being a modern material with special qualities and great application, have become a major support for innovation and growth in many sectors. By lowering structural weight and increasing fuel economy, thermoplastic composites have opened new opportunities for design and manufacturing of aircraft in the aerospace industry. Application of thermoplastic composites not only enhances the safety and economy of cars but also helps the automotive sector to grow towards lightweight and environmental protection.
Thermoplastic composites have progressively replaced conventional materials at the same time in the electronics, medical devices, and construction sectors because of their outstanding electrical insulation, chemical resistance and recyclability, so becoming a major driver in supporting sustainable development. But as the application areas for thermoplastic composites keep growing, the intricacy of their molding technique and the difficulties with manufacturing expenses have progressively surfaced.
Future in-depth research and technological innovations in process optimization, material innovation and cost reduction are essential to overcome these challenges. Simultaneously, as environmental consciousness grows, recycling and life cycle management of thermoplastic composites will also take front stage in future growth. Thermoplastic composites will undoubtedly become more important in future industrial manufacture and help different sectors grow and flourish by means of ongoing technical improvement and application extension.
Feature Product
-
PA12 LCF30 for Drone Fuselages & Wings
What do you know about PA12 LCF30? PA12 ...
-
Competitive Price PA6 LCF30 Composites
What’s it? PA6 LCF30, which stands...
-
ABS CF10 Compound ABS 10%CF Thermoplastic Compo...
What’s ABS CF10? ABS CF10 refers t...