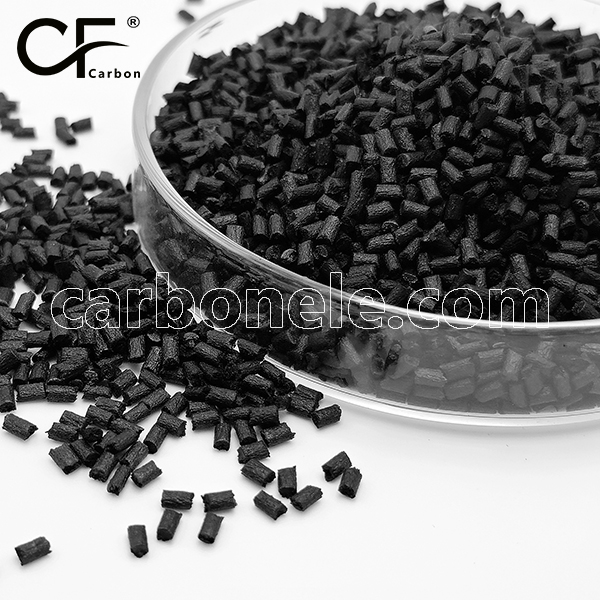
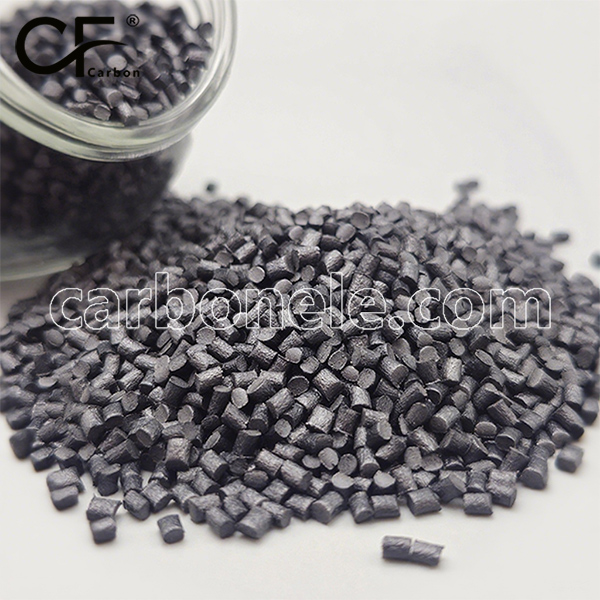
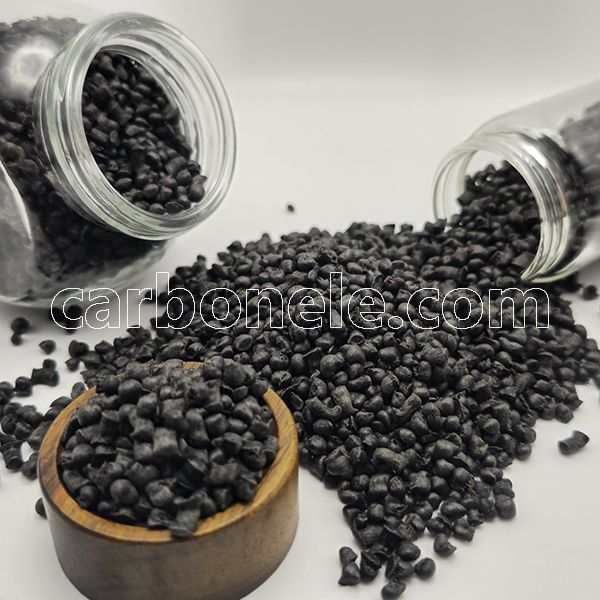
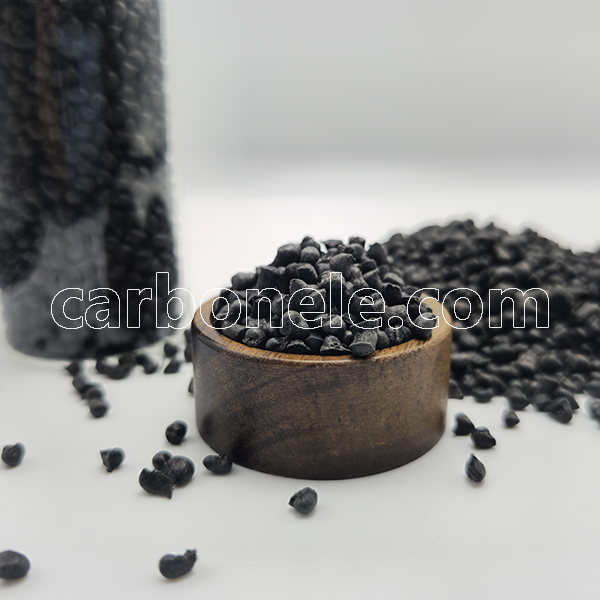
Factory Price ANTISTATIC PA612 CF5 Composites
ANTISTATIC PA612 CF5 composites are materials combining polyamide 6.12 (Nylon 612) with 5% carbon fiber, engineered to dissipate static electricity. They provide enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance, crucial for static-sensitive applications.
- Manufacturer: Carbon New Material
- OEM/ODM: Acceptable
- Color: Black
- Free samples: ≤10kg
- MOQ: 100kg
- Port: Xiamen
- Model: PA612-CF-BCA05
- Features: Anti-static electricity, wear resistance, etc.
What are ANTISTATIC PA612 CF5% Composites?
ANTISTATIC PA612 CF5 composites blend polyamide 612 with 5% carbon fiber reinforcement, designed to dissipate static electricity effectively.
They offer improved mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring static control, such as electronics manufacturing and explosive environments.
These composites ensure operational safety by preventing electrostatic discharge (ESD) that could damage sensitive components or pose hazards.
What are Characteristics and Properties of ANTISTATIC PA612 CF5% Composites?
1. Antistatic Properties:
– The addition of carbon fibers in PA612 CF5 composites imparts antistatic properties to the material.
These composites can effectively dissipate static electricity, reducing the risk of electrostatic discharge (ESD) which can damage sensitive electronic components or ignite flammable materials.
This property is critical in industries such as electronics manufacturing, telecommunications, and explosive environments.
2. Mechanical Strength:
– PA612 CF5 composites exhibit enhanced mechanical properties compared to unreinforced PA612. While the carbon fiber content is relatively low at 5%, it still improves tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance.
This makes the composites suitable for structural applications where mechanical performance is essential.
3. Dimensional Stability:
– Carbon fiber reinforcement helps reduce thermal expansion, enhancing the dimensional stability of PA612 CF5 composites.
They maintain their shape and size over a wide range of temperatures, which is beneficial in applications requiring precise tolerances and minimal dimensional changes.
4. Chemical Resistance:
– PA612 inherently offers good resistance to oils, greases, fuels, and many chemicals. The addition of carbon fibers typically does not compromise this resistance significantly.
PA612 CF5 composites can withstand exposure to various industrial fluids and environments, making them versatile for different application requirements.
5. Electrical Conductivity:
– While not highly conductive like materials with higher carbon fiber content, PA612 CF5 composites may exhibit some level of electrical conductivity due to the presence of carbon fibers.
This conductivity is typically sufficient for static dissipation purposes, ensuring safety in environments prone to static buildup.
6. Heat Resistance:
– PA612 CF5 composites offer good heat resistance, suitable for applications exposed to moderate temperatures. They can withstand thermal cycling without significant degradation, maintaining their mechanical and electrical properties over time.
7. Processability:
– PA612 CF5 composites are compatible with common processing methods such as injection molding and extrusion. They can be molded into complex shapes and sizes, allowing for design flexibility and efficient manufacturing.
8. Surface Finish:
– These composites typically exhibit a smooth surface finish after molding, suitable for applications where aesthetics are important or where minimal post-processing is required.
Which fields will the composites be used in?
Antistatic PA612 CF5 composites find application in various industries and sectors where static dissipation, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance are crucial:
– Electronics: Housings for electronic devices, connectors, and casings where ESD protection is necessary.
– Automotive: Components such as fuel system parts, engine covers, and under-the-hood applications requiring durability and resistance to automotive fluids.
– Industrial Equipment: Static-sensitive components, conveyor systems, and handling equipment where static control is vital for operational safety.
– Packaging: Containers and packaging materials used in explosive or flammable environments to prevent static-related hazards.
– Consumer Goods: Antistatic housings for appliances, tools, and consumer electronics to protect sensitive internal components.
– Textiles: Fibers and fabrics where static buildup needs to be managed to avoid discomfort or safety risks.
Antistatic PA612 CF5 composites offer a balanced combination of antistatic properties, mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance due to the incorporation of carbon fibers into the PA612 matrix.
These properties make them suitable for a wide range of applications across industries where static dissipation and robust material performance are required.
By leveraging these characteristics, manufacturers can achieve reliable and safe solutions for challenging environments and meet stringent regulatory and operational standards effectively.
Content Block 1
Morbi iaculis at quam vel faucibus. Ut semper ipsum ex, quis aliquet justo pretium a. Suspendisse scelerisque metus augue, a interdum leo iaculis sed. Vivamus sit amet nunc odio. Duis vel pulvinar dolor, at lacinia tellus.
Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Suspendisse lacinia quam a elit lobortis tempor


Content Block 1
Morbi iaculis at quam vel faucibus. Ut semper ipsum ex, quis aliquet justo pretium a. Suspendisse scelerisque metus augue, a interdum leo iaculis sed. Vivamus sit amet nunc odio. Duis vel pulvinar dolor, at lacinia tellus.
Pellentesque habitant morbi tristique senectus et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Suspendisse lacinia quam a elit lobortis tempor

Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.