Conductive PAMXD6 CF30 Plastic Raw Materials for Automobile Sensor Housing
Conductive PAMXD6 CF30 is a carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide composite offering high electrical conductivity (10²–10⁵ Ω/sq), exceptional strength (>200 MPa), heat resistance (>200°C), low moisture absorption (<1%), chemical resistance, and lightweight wear resistance.
- Manufacturer: Carbon New Material
- OEM/ODM: Acceptable
- Color: Black
- Free Samples: ≤25kgs
- MOQ: 100kgs
- Port: Xiamen
- Model: MXD6-CF-BCA3
- Fillers: Chopped carbon fiber
Conductive PAMXD6 CF30 is a high-performance polyamide (PAMXD6) composite reinforced with 30% carbon fiber (CF), combining mechanical strength, thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical conductivity.
1. High Electrical Conductivity
Surface resistivity of 10²–10⁵ Ω/sq due to 30% carbon fiber, enabling effective ESD protection and EMI shielding in electronics.
2. Exceptional Mechanical Strength
Tensile strength >200 MPa and high stiffness from carbon fiber reinforcement, suitable for load-bearing structural components.
3. Outstanding Heat Resistance
Heat deflection temperature (HDT) >200°C at 1.82 MPa, maintaining stability in high-temperature automotive and industrial applications.
4. Low Moisture Absorption
Moisture uptake <1% (vs. ~6–10% in standard PA), ensuring dimensional stability in humid or wet environments.
5. Chemical & Hydrolysis Resistance
Resists fuels, oils, acids, and alkalis, making it ideal for automotive fuel systems and chemical processing equipment.
6. Lightweight & Wear-Resistant
Carbon fiber reduces weight vs. metals while improving abrasion resistance for gears, bearings, and moving parts.
Key applications of PAMXD6 CF30 include:
| Application Field(PAMXD6 CF30) | Specific Use Category | Example Products & Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Electrical | ESD Components | Semiconductor trays, PCB fixtures – Prevents static damage with 10²–10⁵ Ω/sq resistivity |
| EMI Shielding | 5G device housings, automotive connectors – Blocks electromagnetic interference | |
| Sensor Components | Industrial/automotive sensor enclosures – Conductive protection for sensitive electronics | |
| Automotive | Under-the-Hood Parts | Throttle bodies, bearing housings – Lightweight metal replacement, withstands >180°C |
| Fuel Systems | Fuel lines, connectors – Resists hydrocarbons/hydrolysis for long-term durability | |
| EV Components | Battery brackets, charging ports – Flame-retardant grades meet safety standards | |
| Industrial Machinery | Wear-Resistant Parts | Gears, bearings, slides – Carbon fiber reduces friction, extends service life |
| Chemical Equipment | Pump/valve components – Acid/alkali-resistant for corrosive environments | |
| Aerospace & Defense | Drone/UAV Structures | Lightweight frames, joints – Conductive & high strength-to-weight ratio |
| Satellite Components | Non-metallic structural parts – Prevents charge buildup in space applications | |
| Specialty Applications | Medical Devices | Sterilizable instrument housings – Withstands gamma/autoclave sterilization |
| Sports Equipment | Bicycle frames, tennis rackets – High-strength, vibration-damping performance |
Note: Performance may vary based on processing conditions and additional additives (e.g., flame retardants).
Key Properties of PAMXD6 CF30
- Conductivity: Surface resistivity ~10²–10⁵ Ω/sq (ESD/EMI-compliant). - Mechanical: Tensile strength >200 MPa. - Dimensional Stability: Low moisture absorption (<1% vs. standard PA). - Tensile strength >200 MPa - Heat deflection temperature (HDT) >200°C at 1.82 MPa - Moisture uptake <1% (vs. ~6–10% in standard PA)
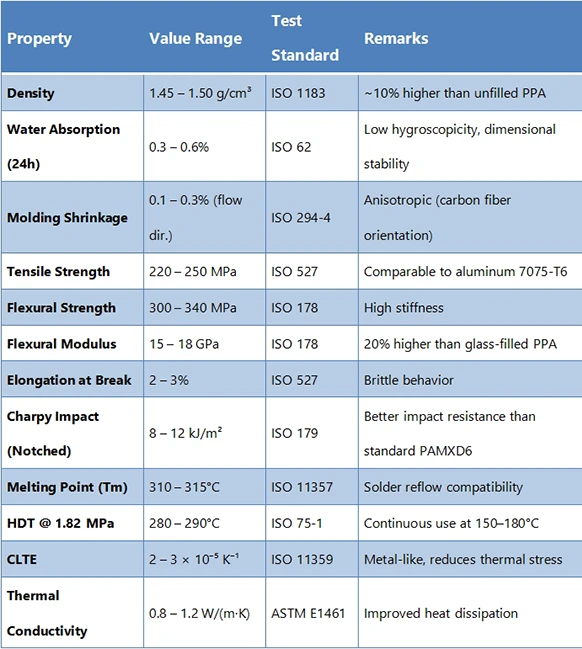
Surface Resistivity Comparison
Conductors < 10⁵ Ω/sq. Antistatic Materials 10⁵ ~ 10¹² Ω/sq. Insulators > 10¹² Ω/sq. Static-Dissipative 10⁶ ~ 10¹¹ Ω/sq. *Key Influencing Factors Humidity: Increased moisture can reduce resistivity (e.g., in polymers). Temperature: Affects carrier mobility (↑ heat may lower semiconductor resistivity). Surface Contamination: Dust/oils alter readings significantly. Additives: Carbon black, metallic fillers can lower resistivity. *Applications Electronics: Antistatic materials (10⁶–10⁹ Ω/sq) prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD). Aerospace: Composites must control resistivity to avoid charge buildup. Medical Devices: Insulating materials (>10¹² Ω/sq) ensure patient safety. *Examples Polypropylene (PP): ~10¹⁶ Ω/sq (excellent insulator). Carbon Fiber Composites: 10³–10⁶ Ω/sq (static dissipation). ESD Flooring: 10⁶–10⁹ Ω/sq.
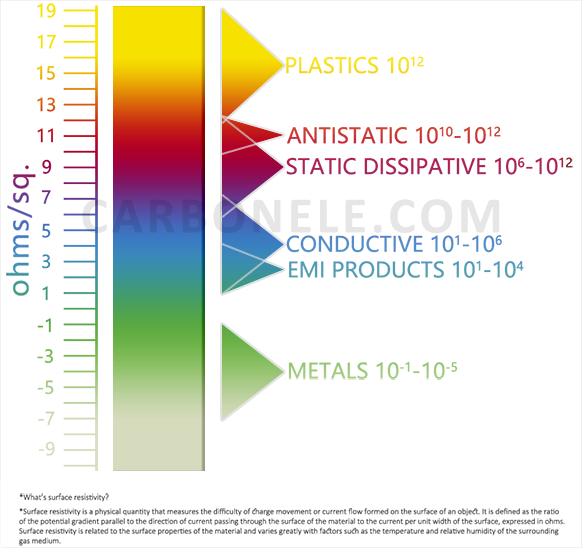
Get to Know Carbon Fibers
The table presents key performance data of carbon fiber grades. T300, with a tensile strength of 3530 MPa and a tensile modulus of 230 GPa, has a relatively low tensile elongation at break of 1.5% and a body density of 1.76 g/cm³. As the grade increases, for example, T700S shows an enhanced tensile strength of 4900 MPa compared to T300, while maintaining the same tensile modulus but with a higher elongation at break of 2.1%. T800S and T1000G both have a tensile modulus of 294 GPa, and their tensile strengths are 5880 MPa and 6370 MPa respectively. T1100G stands out with the highest tensile strength of 7000 MPa and a tensile modulus of 324 GPa. Generally, with the increase in product grade, the tensile strength and modulus tend to rise, while the density remains relatively stable around 1.8 g/cm³.
How to Buy?
If you want to obtain information such as product specifications, performance, and price, choose a suitable product according to your own needs. Meanwhile, you can ask the manufacturer to provide samples for testing to ensure that the material meets your usage requirements. If you are interested in purchasing this composite material, please contact the manufacturer Carbon (Xiamen) New Material directly.



Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.