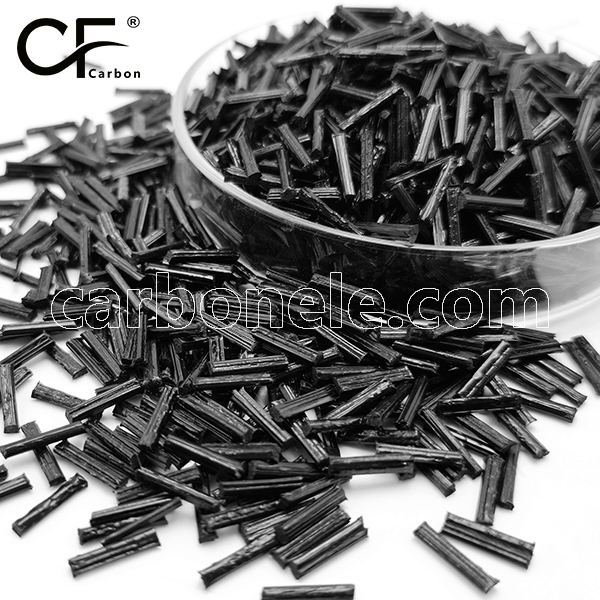
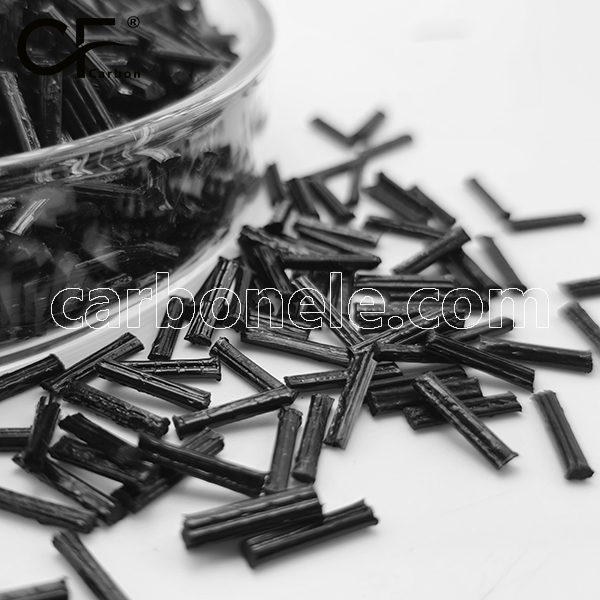
Best Price PA6 LCF50 50% Carbon Fiber NYLON 6 Composites
PA6 LCF50 composites are polyamide 6 materials reinforced with 50% long carbon fibers. They offer high strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for applications requiring superior mechanical performance, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
- Manufacturer: Carbon New Material
- OEM/ODM: Acceptable
- Color: Black
- Free Samples: ≤25kgs
- MOQ: 100kgs
- Port: Xiamen
- Model No.: PA6-LCF-BCA5
What’s it?
PA6 LCF50 composites are polyamide 6 (PA6) materials reinforced with 50% long carbon fibers (LCF).
This composition results in composites with exceptional mechanical properties, including high strength, stiffness, and impact resistance.
The long carbon fibers are uniformly dispersed within the polymer matrix, enhancing dimensional stability and reducing warping.
The composites are lightweight yet robust, making them suitable for applications where weight reduction and superior performance are critical, such as automotive, aerospace, and sports equipment industries.
Their enhanced heat resistance and chemical resilience further expand their utility in demanding environments requiring durability and reliability.
Why to choose it?
Features
1. High Strength and Stiffness: PA6 LCF50 composites exhibit superior mechanical properties due to the 50% long carbon fiber reinforcement.
This results in increased tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance compared to traditional nylon 6 materials.
2. Lightweight: Despite the high fiber content, PA6+LCF50 remains lightweight, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical without compromising on strength.
3. Dimensional Stability: The presence of carbon fibers enhances dimensional stability, reducing warping and deformation under load and temperature variations.
4. Chemical Resistance: Nylon 6 inherently offers good chemical resistance, and the addition of carbon fibers further enhances this property, making PA6 LCF50% suitable for environments with exposure to various chemicals.
5. Enhanced Heat Resistance: Carbon fibers contribute to improved heat resistance of the composite, making it suitable for applications requiring thermal stability.
Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing PA6 LCF50 composites involves several key processes:
1. Melt Mixing: Nylon 6 resin and carbon fibers are mixed together in a melt mixing process to ensure uniform dispersion of the fibers within the polymer matrix.
2. Compounding: The mixed materials undergo compounding to further blend and distribute the carbon fibers evenly, enhancing the mechanical properties of the composite.
3. Molding: The compounded material is then processed using injection molding or compression molding techniques to form the desired shape or component.
4. Post-Treatment: Some applications may require additional post-treatments such as surface treatments or coatings to improve adhesion, aesthetics, or specific functional properties.
Applications
PA6 LCF50 composites find diverse applications across various industries:
1. Automotive: Used in structural components such as engine mounts, under-the-hood parts, and interior components where high strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties are crucial.
2. Aerospace: Components in aircraft interiors, structural panels, and other critical parts benefit from PA6 LCF50’s combination of strength, stiffness, and weight savings.
3. Sports and Recreation: Sporting goods such as bicycle frames, tennis rackets, and snowboards utilize PA6 LCF50 for its durability, impact resistance, and lightweight characteristics.
4. Industrial Equipment: Machinery parts, conveyor systems, and industrial components benefit from the high mechanical strength and wear resistance of PA6 LCF50% composites.
5. Electronics: Enclosures and structural components in electronic devices benefit from the lightweight and structural integrity provided by PA6 LCF50.
What are the development trends?
1. Advanced Additive Manufacturing: Increasing adoption of additive manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing for producing PA6+LCF50 components, enabling complex geometries and customized designs.
2. Recycling and Sustainability: Growing focus on recycling carbon fiber-reinforced composites to reduce environmental impact and meet sustainability goals.
3. Hybrid Composites: Exploration of hybrid composites combining PA6 LCF50% with other materials like glass fibers or thermoplastics to achieve specific performance requirements.
4. Smart Manufacturing: Integration of sensors and IoT technologies in manufacturing processes to monitor and optimize the performance of PA6 LCF50 composites in real-time.
5. Cost Efficiency: Efforts towards optimizing manufacturing processes and raw material costs to make PA6 LCF50 composites more competitive in price while maintaining high performance.
PA6 LCF50 composites represent a significant advancement in material technology, offering enhanced mechanical properties, lightweight design, and versatility across a wide range of demanding applications.
As technology and manufacturing techniques continue to evolve, PA6 LCF50 is poised to play a crucial role in the next generation of lightweight, high-performance materials in automotive, aerospace, and beyond.
Read more on long carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastics, please click here or feel free to contact us.
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
PA6 LCF50 composites exhibit exceptional mechanical properties: 1. High Tensile Strength: Enhanced by the 50% long carbon fiber reinforcement. 2. Stiffness: Greater rigidity compared to traditional polyamide 6. 3. Impact Resistance: Improved ability to withstand sudden shocks or impacts. 4. Lightweight: Despite high fiber content, maintains a lightweight profile. 5. Dimensional Stability: Minimizes warping or deformation under load and temperature variations.


Frequently Asked Questions
Carbon (Xiamen) New Material Co., Ltd. aims to provide buyers with "one-stop" worry-free high-quality services. Here you can find all information about carbon fiber engineering plastics. If you still have questions, please send us an email for consultation!
-
How can I contact the manufacturer of a product that interests me?
When you find a product you are interested in, you can contact the manufacturer directly by sending an email and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
-
How do I find the products that interest me?
All you need to do is enter the keyword, product name in the search window and press the Enter key on your keyboard. Your search results page will then be displayed. You can also search within the product category pages on the home page. Each category is divided into subcategories, allowing you to refine your search and find products that interest you.
-
Where will I find a buying guide?
Please contact our after-sales service directly and we will provide you with a comprehensive operating guide.
-
What are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites are materials where carbon fibers are incorporated into a thermoplastic matrix. They combine the strength and stiffness of carbon fibers with the processability and recyclability of thermoplastics. For instance, they are used in automotive parts like bumper beams.
-
What are the benefits of CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites over traditional composites?
The key benefits include faster production cycles, easier recyclability, and better impact resistance. They also offer design flexibility. An example is in the manufacturing of consumer electronics casings where complex shapes can be achieved more easily.
-
How are CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites processed?
Common processing methods include injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding. Injection molding is widely used for mass production. For example, in the production of small components for the medical industry.
-
What industries use CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
They are utilized in aerospace, automotive, medical, and sports equipment industries. In aerospace, they can be found in interior components. In the medical field, they might be used in prosthetics.
-
How does the carbon fiber content affect the properties of the composites?
Higher carbon fiber content generally leads to increased strength and stiffness but may reduce ductility. A moderate content is often balanced for specific applications. For example, a higher content might be preferred in structural parts of a race car.
-
What are the challenges in using CF Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites?
Challenges include higher material costs, complex processing equipment requirements, and ensuring uniform fiber dispersion. Issues with adhesion between the fibers and the matrix can also arise. An example is in achieving consistent quality in large-scale production.